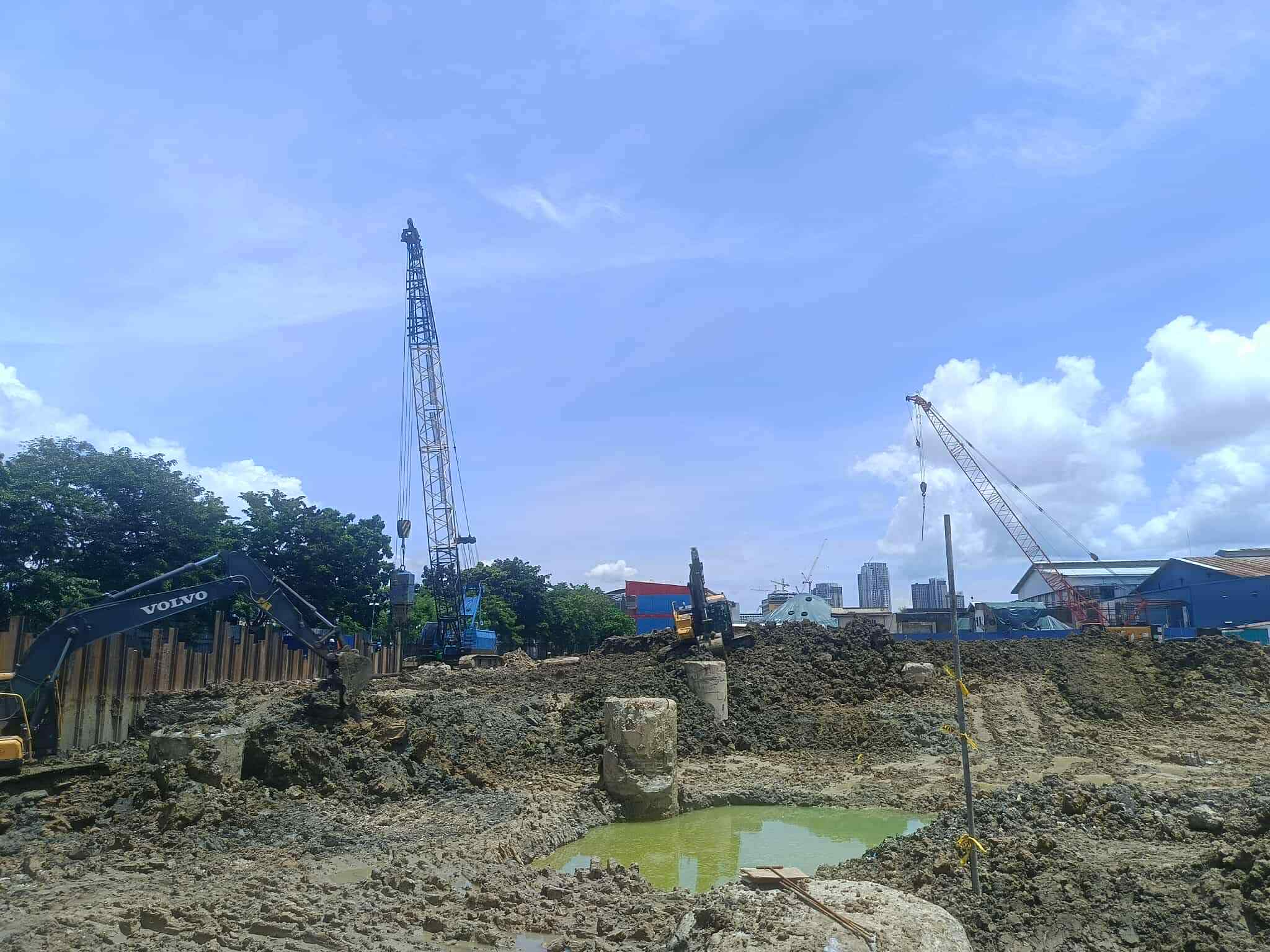
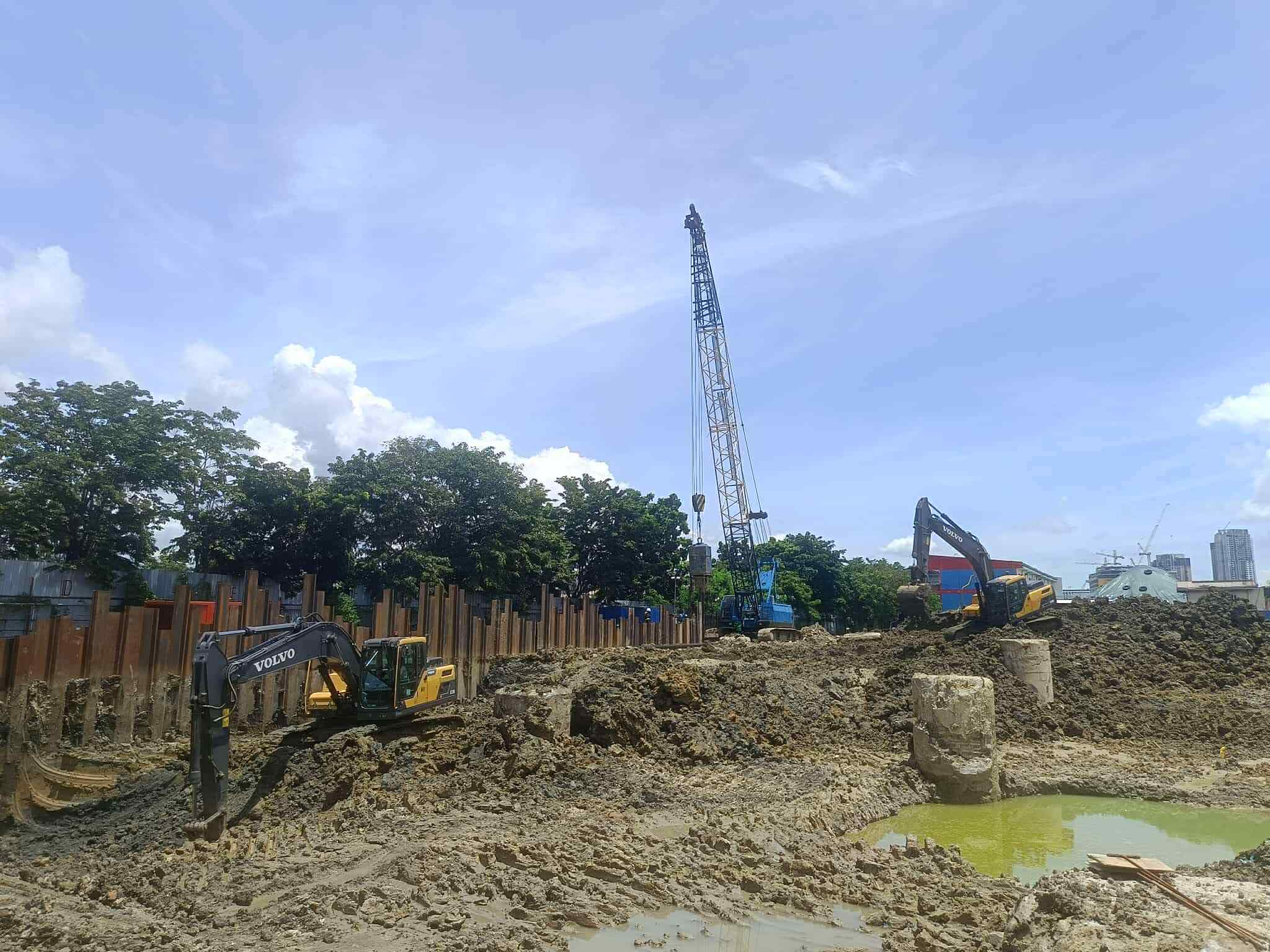
Driving Deep: The Advantages of Prestressed Concrete Piles
In the world of construction, a solid foundation is paramount. When dealing with challenging soil conditions or the need for heavy load-bearing capacity, prestressed concrete piles stand out as a robust and reliable solution. This blog post explores the key benefits and applications of these essential structural elements.
What are Prestressed Concrete Piles?
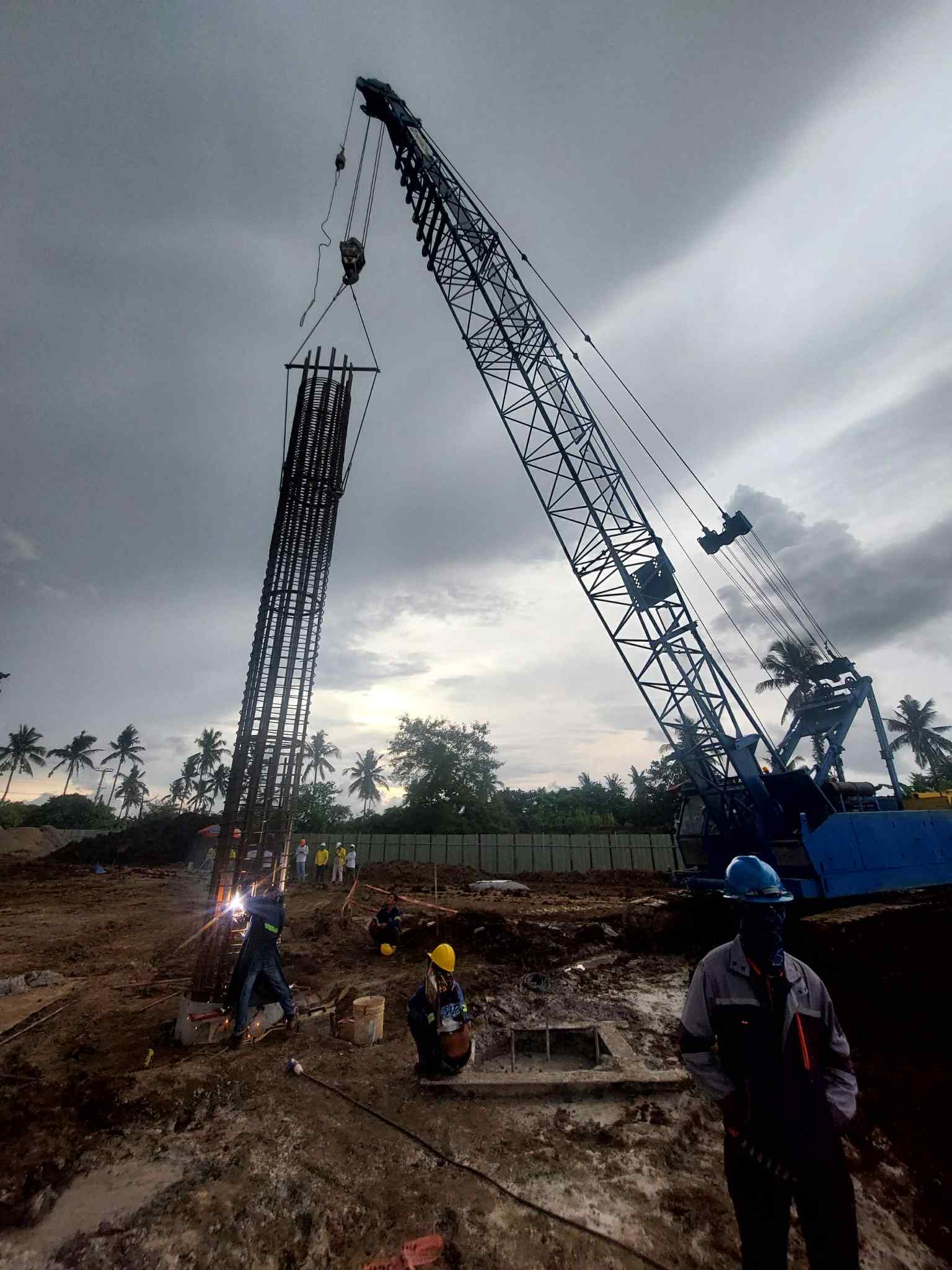
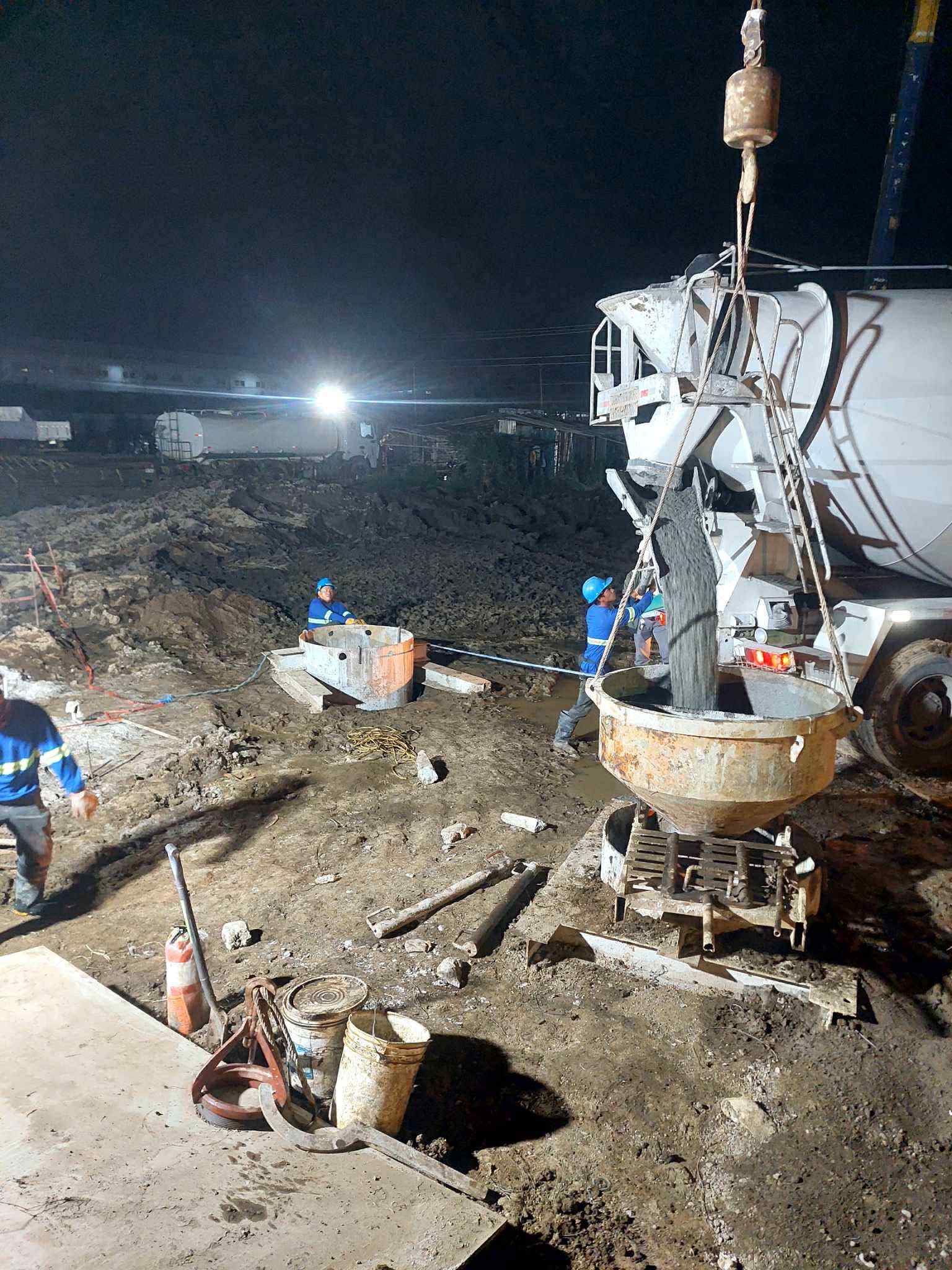
Prestressed concrete piles are high-strength concrete piles that incorporate prestressing steel tendons or wires. These tendons are tensioned before or after the concrete is cast, creating internal compressive stresses within the pile. This prestressing process significantly enhances the pile’s strength, durability, and load-bearing capacity compared to conventionally reinforced concrete piles.
Types of Prestressed Concrete Piles:
- Pre-tensioned Piles: The tendons are tensioned before the concrete is poured. The concrete is then cast around the tensioned tendons. Once the concrete hardens, the tendons are released, transferring the prestress to the concrete through bond.
- Post-tensioned Piles: Ducts are cast into the concrete pile, and the tendons are inserted after the concrete has hardened. The tendons are then tensioned and anchored, transferring the prestress to the concrete.
Key Advantages of Prestressed Concrete Piles:
- High Load-Bearing Capacity: The prestressing process significantly increases the pile’s resistance to bending and cracking, allowing it to support heavier loads compared to traditional piles.
- Enhanced Durability: The internal compressive stresses induced by prestressing help to counteract tensile stresses caused by external loads and environmental factors, reducing the risk of cracking and improving resistance to corrosion and weathering. This makes them ideal for marine environments and areas with aggressive soil conditions.
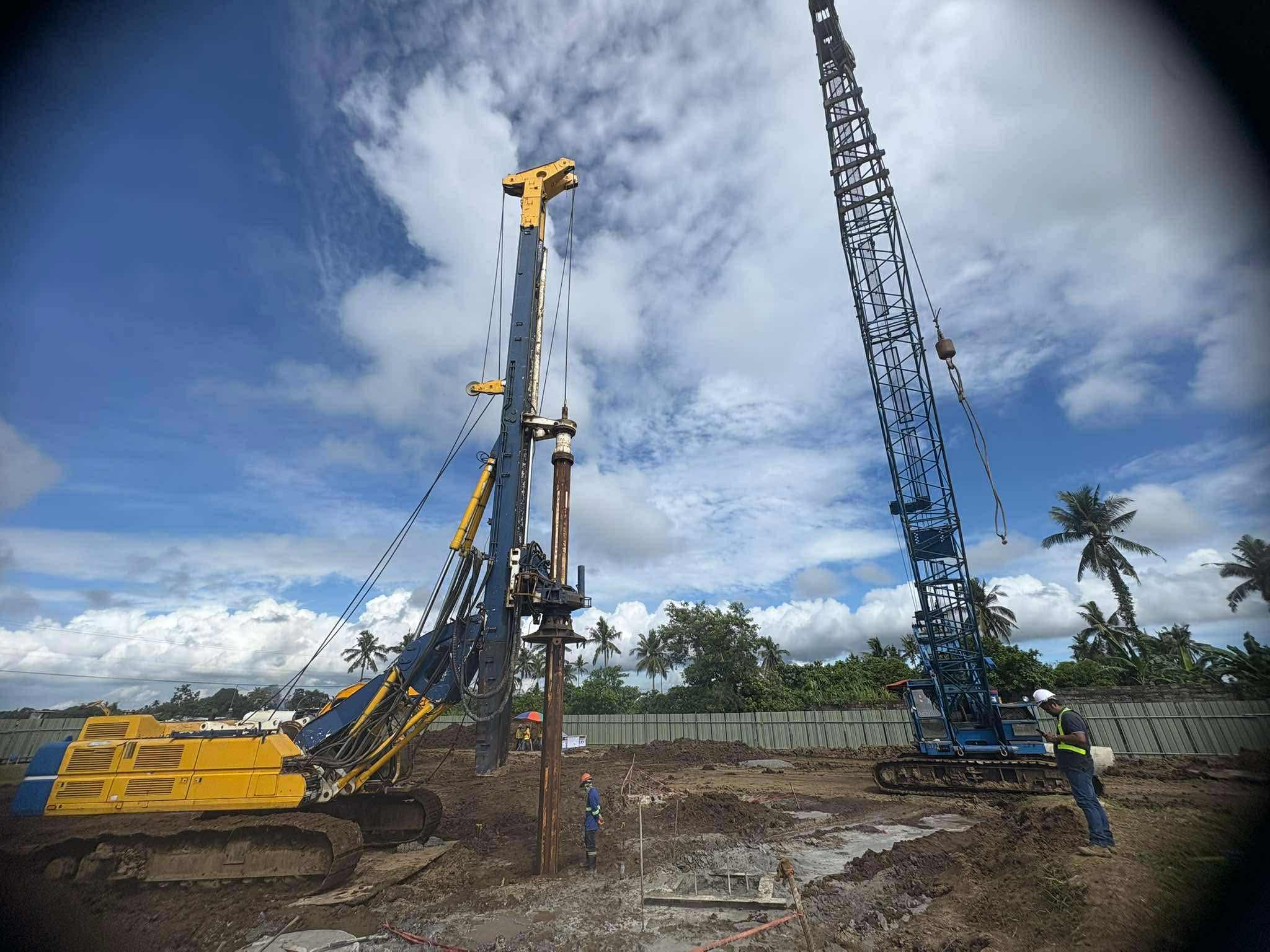
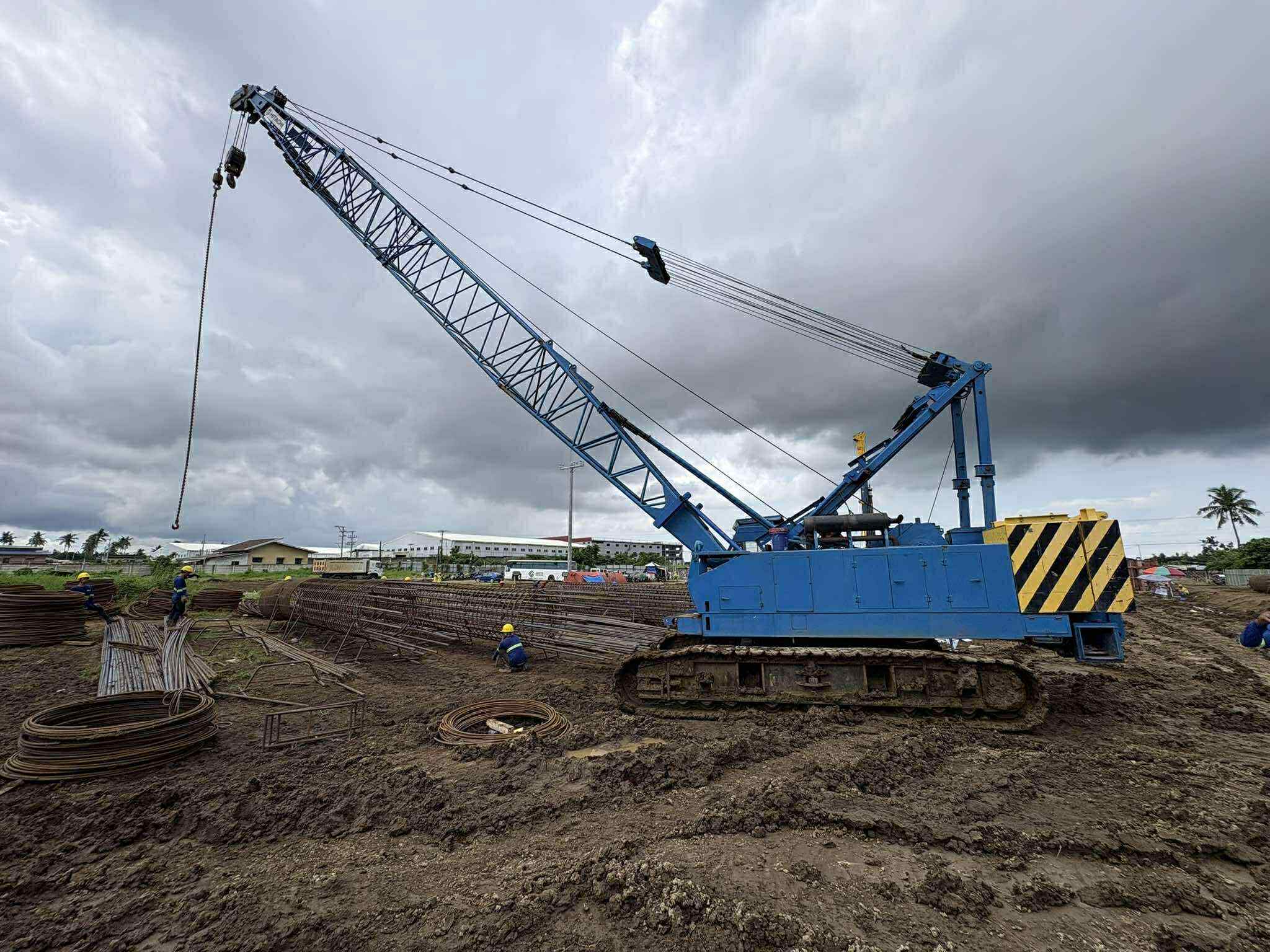
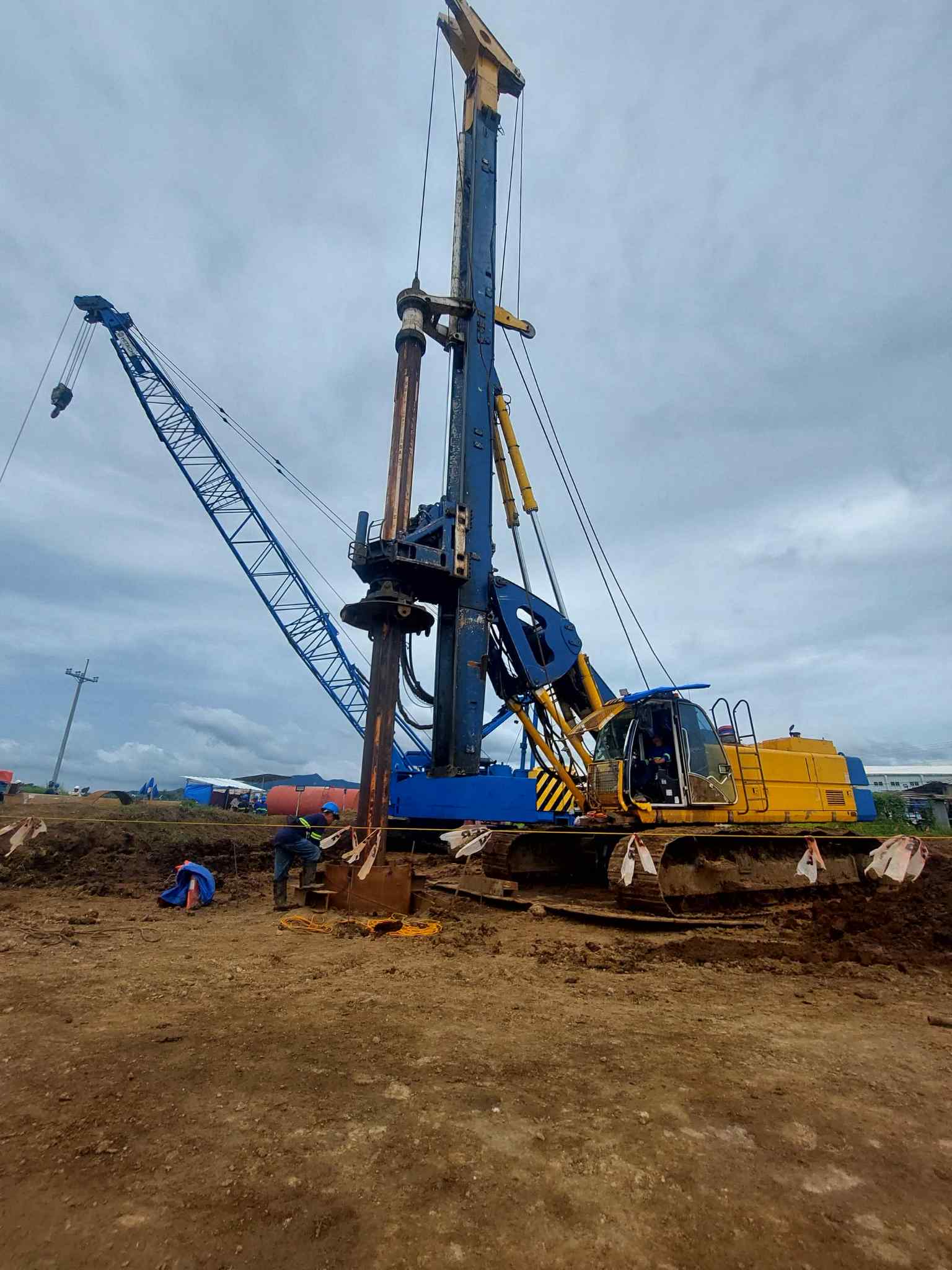
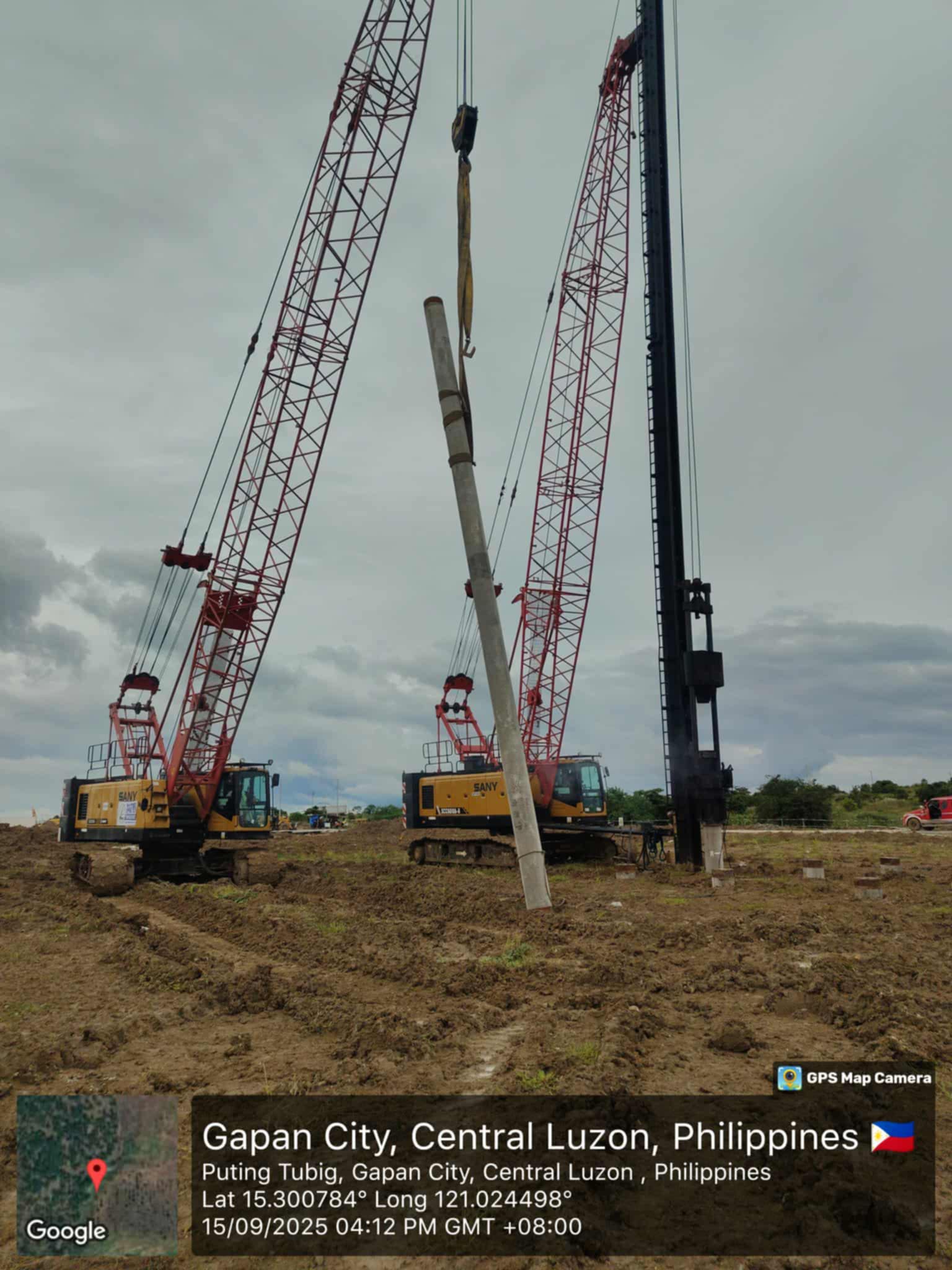
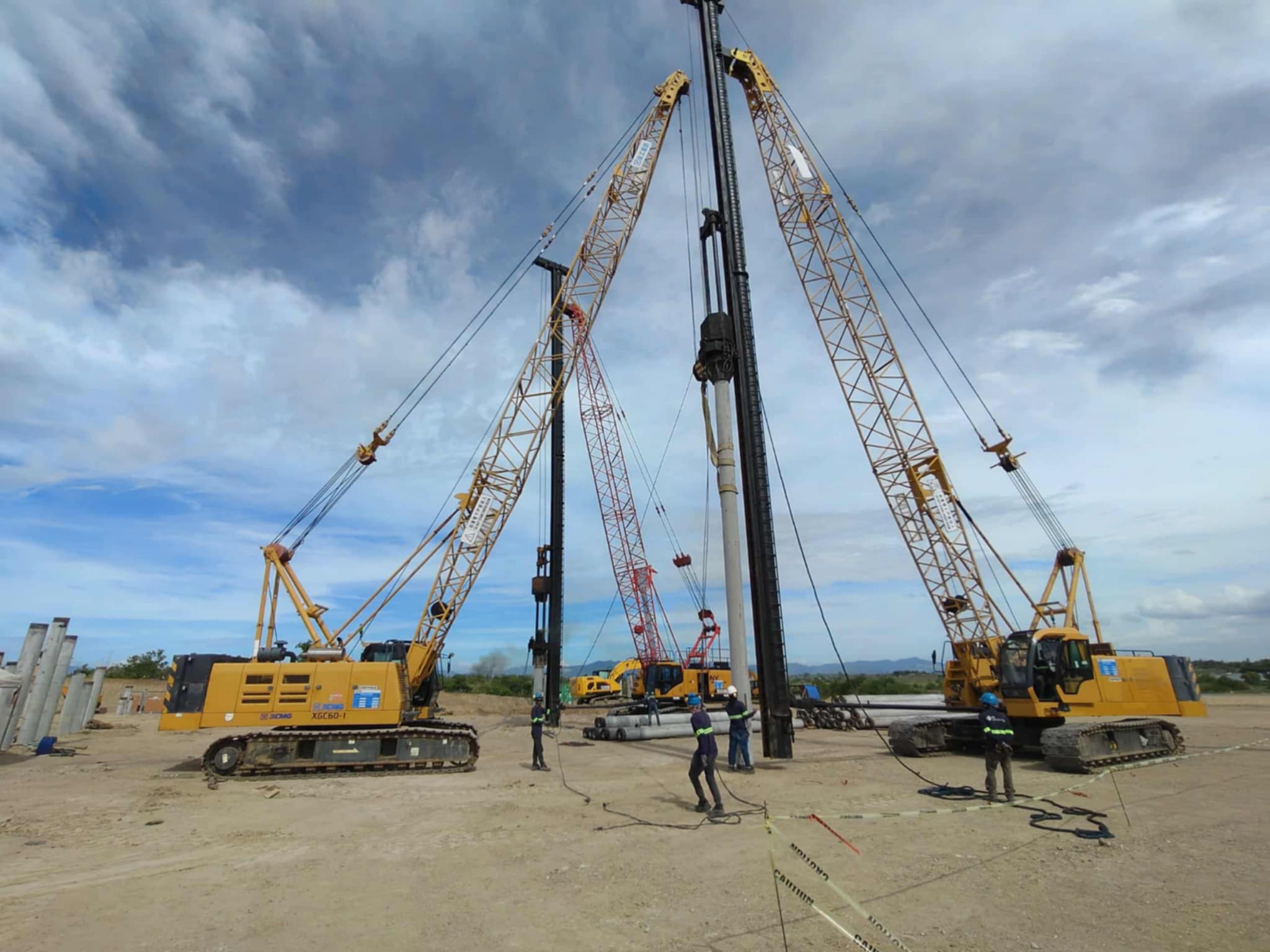
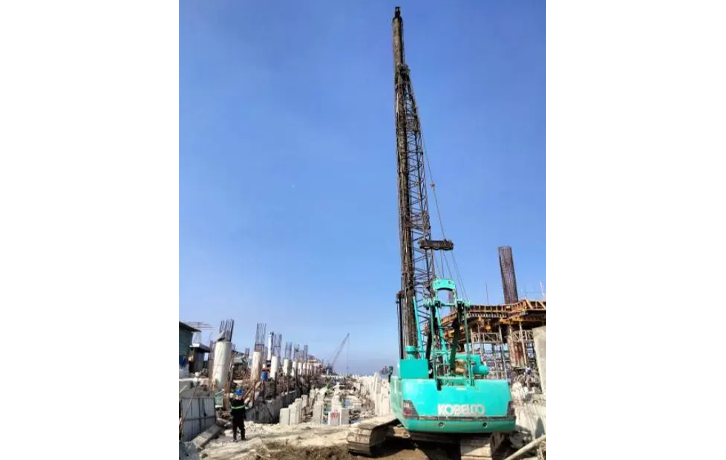
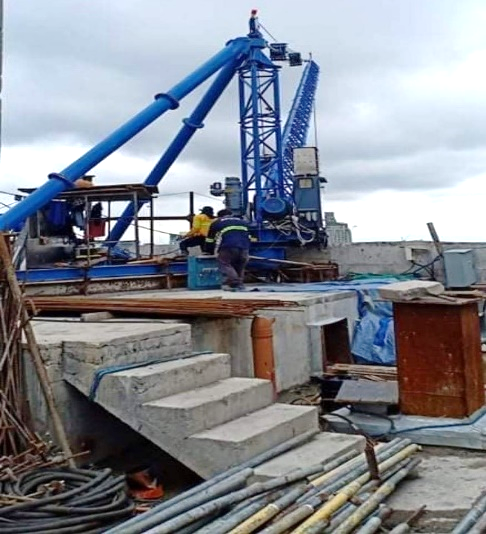
- Improved Handling and Driving: Prestressed piles are less susceptible to damage during handling and driving due to their increased strength and resistance to cracking. This leads to reduced wastage and faster installation.
- Reduced Cross-Section: For a given load capacity, prestressed piles can often have a smaller cross-section than conventionally reinforced piles, which can be advantageous in situations with limited space or when minimizing excavation is desired.
- Greater Length Capacity: Prestressed piles can be manufactured in longer lengths, reducing the need for splicing and improving overall structural integrity.
- Resistance to Bending and Cracking: The prestress significantly increases the pile’s resistance to bending and cracking, which is crucial in situations with lateral loads or seismic activity.
Applications of Prestressed Concrete Piles:
Prestressed concrete piles are widely used in a variety of construction projects, including:
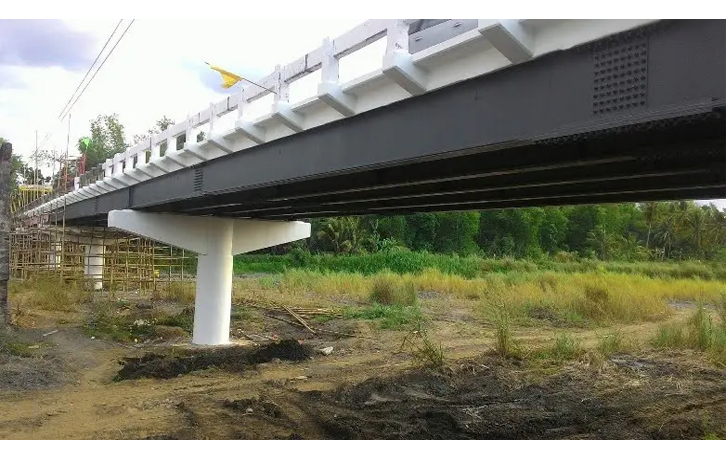
- Bridges and Overpasses: Providing strong and stable foundations for heavy traffic loads.
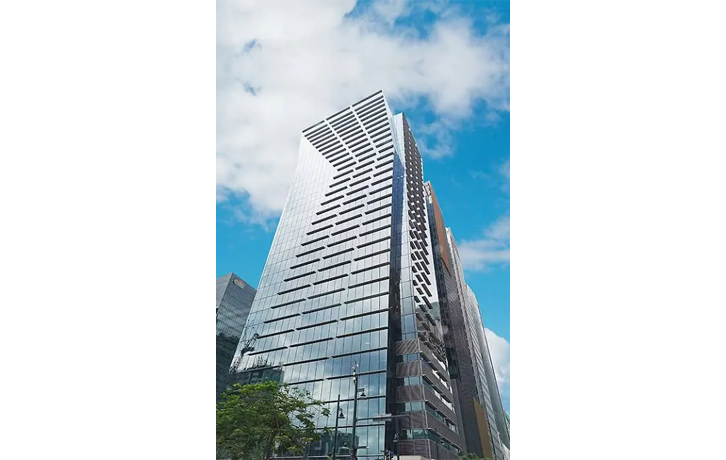
- High-Rise Buildings: Supporting the immense weight of tall structures.
- Marine Structures: Resisting the corrosive effects of saltwater and wave action in piers, docks, and offshore platforms.
- Industrial Facilities: Supporting heavy machinery and equipment.
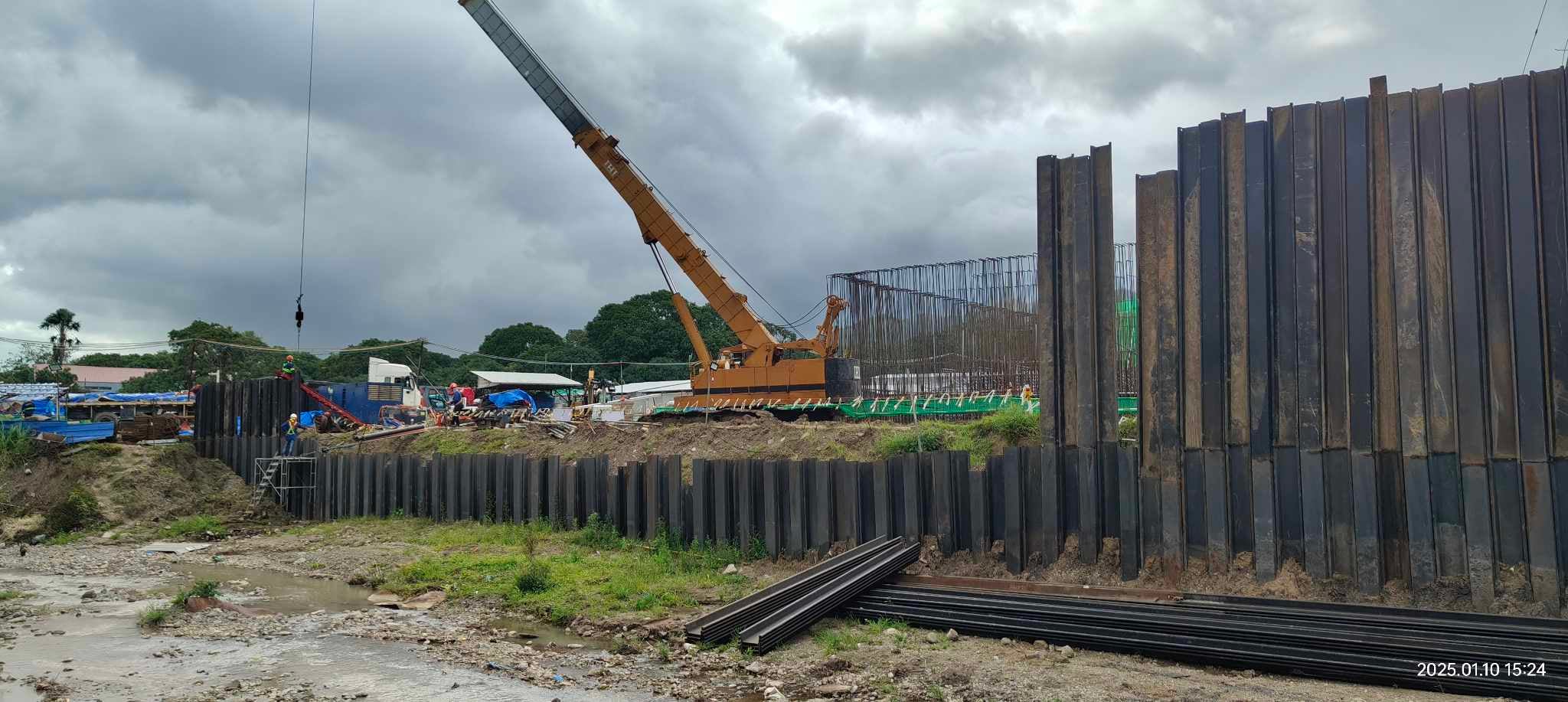
- Retaining Walls: Providing stability against soil pressure.
- Power Plants: Supporting heavy equipment and structures.






























































































































































































































































































































































Leave A Comment